Abstract
Introduction: Gene expression profiling (GEP) of purified CD138+ bone marrow plasma cells (PC) in patients with newly diagnosed multiple myeloma (MM) has proven to be a reliable prognostic tool. In this study, we aimed to describe the clinical outcomes of all consecutive NDMM patients with available GEP pre-treatment and compare GEP with standard FISH in determining relapse free survival (RFS) and overall survival (OS).
Methods: From April 2014 until January 2017, we identified 104 patients with NDMM who had baseline GEP70 analysis at our institution. GEP70 was performed using CD138+ cells from bone marrow samples at diagnosis through MyPRS® (Signal Genetics, Little Rock, AR). Fisher's exact test was used to evaluate the associations between two categorical variables. The Wilcoxon rank sum test was used to evaluate the difference in continuous variables between patient groups. Kaplan-Meier method was used to estimate the time to event endpoints including RFS and overall survival (OS). The log-rank test was used to evaluate the differences in the time to event endpoints between different risk group categories. Univariate Cox proportional hazards model was used to evaluate the association between a continuous variable and RFS/OS. Statistical software SAS 9.3 (SAS, Cary, NC) and S-Plus 8.2 (TIBCO Software INc., Palo Alto, CA) were used for all analysis.
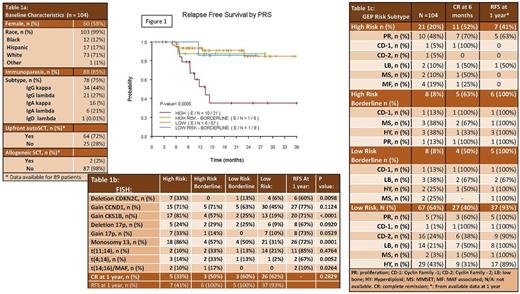
Results: Median age was 63 (37-89) (Table 1a). Patients presented with lytic lesions (78%), anemia (78%), kidney dysfunction (13%) and hypercalcemia (31%). One patient did not meet CRAB criteria or biomarkers of malignancy, but had severe recurrent infections attributed to underlying myeloma requiring initiation of systemic therapy which prompted resolution of infections. One patient was initiated on therapy based on an i:u sFLC ratio of 165. All patients with available data for initial treatment (n=101), were treated either with bortezomib (63%), carfilzomib (37%) in combination with lenalidomide (86%) or cyclophosphamide (14%) and dexamethasone (100%). All patients received at least a three-drug combination as initial treatment, with 73% of patients receiving an upfront autologous transplant. Upfront autoSCT improved RFS (n=9/66; 14%) compared to non- or delayed autoSCT (n=8/25; 32%; p=0.03) but did not affect OS (p=0.86). Two patients (2 %) proceeded to an upfront allogeneic transplant as part of a clinical trial. With up to 36 months of follow up (range 0.9-35.9 months), 74% of patients are relapse free and 86% of patients are alive (Table 1b). GEP risk category predicted RFS (p=0.0005) in this series of patients (Figure 1). Table 1c shows GEP risk subtypes with clinical outcomes and association to FISH abnormalities. Uniformly, patients with high risk FISH abnormalities and low risk GEP had better clinical outcomes than patients with high risk GEP. High risk GEP patients represented 20% of all NDMM in this cohort. At one year, about 50% of these patients had relapsed or died compared to only 5% of patients in all of the other categories of GEP. By FISH, only t(14;16) predicted RFS (p=0.0001). Neither FISH nor GEP significantly predicted OS (P>0.05) although there were trends for worse survival for high risk GEP and FISH t(14;16).
Conclusion: In this cohort of NDMM patients treated with modern therapies with most patients having received an autoSCT, GEP risk profiling was one of the best predictors of RFS. Longer follow up will be needed to determine prediction of OS in this cohort of patients.
Lee: Eutropics Pharmaceuticals: Research Funding; Adaptive: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Pimera Inc: Consultancy; Celgene: Consultancy; Takeda: Consultancy; Daiichi Sankyo: Research Funding. Patel: Pfizer: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Juno: Consultancy; Celgene: Consultancy. Thomas: Celgene: Research Funding; Bristol Myers Squibb: Research Funding. Neelapu: Merck: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Bristol-Myers Squibb: Research Funding; Celgene: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Karus: Research Funding; Cellectis Inc.: Research Funding; Kite Pharma: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Novartis: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Poseida Therapeutics, Inc: Research Funding. Orlowski: BioTheryX: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Manasanch: adaptive biotechnologies: Consultancy; quest diagnostics: Research Funding; sanofi: Research Funding; merck: Research Funding; celgene: Consultancy; takeda: Consultancy.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal